扫一扫 添加小助手
服务热线
13818320332
扫一扫 关注我们
 Product or Component Bioburden
Product or Component Bioburden
产品或部件生物负荷
Product or component bioburden monitoring is not considered part of all environmental monitoring programs. Bioburden testing is performed on a non-sterile product to determine its microbial load. The intended use of the product, the nature of the product (growth promoting product which is held during processing), or the manufacturing process used may dictate the establishment of acceptance levels and the exclusion of objectionable microorganisms. Listed below are some factors that may impact product or component bioburden:
产品或部件生物负荷监测并不是所有环境监测项目的一部分。生物负荷测试在非无菌产品上进行,以确定其微生物负荷。产品的预定用途、性质(加工过程中促进产品成型)或制造工艺的使用均可决定其验收等级或对不良微生物的排除。以下列出的是可能会造成产品或部件生物负荷的一些因素:
• Raw material source: Bioburden may range from very high (derived from natural sources) to zero.
原料来源:生物负荷的范围很广,可以很高(源于天然资源),也可以为零。
• Water: It is often the highest volume raw material in product formulations.
水:水通往是产品配方中量最多的一种原料。
• Components: Various grade glass or plastic components can be obtained either sterile or non-sterile.
部件:各种高档玻璃或塑料部件可灭菌或未灭菌。
• Manufacturing environment: It should not adversely affect product quality.
生产环境:生产环境可能对产品质量产生不利的影响。
• Processing of formulation: Formulations incorporating filtration steps or requiring heating for dissolution may reduce bioburden. Other manufacturing steps such as timed storage at ambient temperature may increase bioburden.
配方工艺:将配方纳入过滤步骤,或者加热散发可能会降低生物负荷。而其他生产步骤,如在常温下将其定时存储则会增加生物负荷。
• Equipment: The equipment used and its level of cleanliness will impact final product bioburden.
设备:所使用设备的洁净程度会影响产品最终的生物负荷。
Antimicrobial activity: The presence of preservatives and the antimicrobial properties of the raw materials used will determine the formulation susceptibility to contamination.
抗菌活性:配方对污染的敏感度取决于防腐剂的存在和原材料的抗菌性能。
• Water activity: Water activity (a determinant in preservative selection) is an indicator of formulation susceptibility to contamination.
水活性:水活性(选择防腐剂的决定因子)是配方对污染的敏感度的标志。
Determination of Product or Component Bioburden
产品或部件生物负荷确认
Product or component bioburden levels may be determined through various test methods. Some methods are listed below:
产品或部件生物负荷级别可通过各种测试法来确定。方法如下:
Pour plating倾倒平板法
Spread plating涂布平板法
Membrane filtration膜过滤法
Most Probable Number (MPN) 最大或然数法
Automated rapid microbiology systems自动化快速微生物系统法
The test method used will be based on the level of sensitivity necessary to: (a) meet the established acceptance criteria, and (b) neutralize any anti-microbial property that may be inherent to raw materials or as a result of added preservatives. Some automated rapid microbiology systems give higher counts than manual methods, since they may include counts of non-culturable or injured organisms.
测试使用的方法根据敏感度级别,需做到以下两方面:1)符合既定的验收标准 2)中和任何原料固有的或因添加防腐剂产生的抗菌性能。一些自动化快速微生物系统法比手工方法更高效,因为它们包括无数可培养或受伤的生物。
All relevant factors must be considered when establishing acceptance criteria for product and component bioburden. An acceptable bioburden level is that which does not adversely affect product quality.
在建立产品和部件生物负荷验收标准时,一切相关因素都必须考虑在内。一个可接受的生物负荷标准不影响产品质量。
For many terminally sterilized products, bioburden counts alone do not provide sufficient information. It also may be necessary to assess the thermoresistance, or D-value, of the bioburden. Total bioburden counts that are within limits may cause a significant problem if the bioburden exceeds the thermoresistance anticipated for the sterilization model.
对许多最终已灭菌产品来说,生物负荷数本身并不能提供足够的信息。同时,评估生物负荷的抗热性或D值也是必要的。如果总限度内生物负荷数超过灭菌模式预期的抗热性,将引发重要问题。
D-values can be determined using sophisticated equipment (thermoresistometer) with square wave heating, with heat-up and cooling times less than or equal to 10 seconds. For routine screening of bioburden, a heat shock or boiling water test can be used to rule out the presence of organisms exceeding a predetermined D-value.
使用先进的设备(热阻计)与方波加热便可确定D值,升温时间和冷却时间均不超过10秒。对于微生物负荷的常规筛选,一次热震或沸水测试即可排除超出预定D值的生物体。
Parametric Release and Bioburden 参数放行和生物负荷
The acceptance of parametric release by the FDA in 1985 increased the importance of bioburden testing, characterization, and resistance of recovered microorganisms. FDA Compliance Policy Guide 7132a.13 issued in 1987 details the necessary criteria for parametric release. As defined in the policy guide, parametric release is a sterility release procedure based upon effective control, monitoring, and documentation of a validated sterilization process cycle in lieu of release based upon end-product sterility testing.
1985年,美国食品及药物管理局于对参数放行的接受增加了生物负荷的测试、特性的重要性,以及复原微生物体的抵抗力。1987年实施的FDA认证政策指南中详细规定了参数放行的必要标准。政策指南中指出,参数放行是一套灭菌放行程序。它根据有效的控制和监测,以及一份有法律效力的灭菌工艺文件,替代了以终端产品灭菌测试来放行的方法。
Major emphasis is placed on the resistance of recovered spore formers. Recovered spore formers with greater resistance than the indicator organism used in the cycle validation would render the batch non-sterile in terms of the guidance.
现已非常重视复原的芽孢菌类阻力。循环验证中复原的芽孢菌类阻力比指示有机物大时,从指南方面来说此批为无菌。
In-Process Testing 过程中培训
In-process environmental monitoring samples may be taken to evaluate:
对过程中环境监测样本可以采取如下评估:
• The ability of the equipment to perform within specified environmental quality standards
设备能在规定的环境质量标准内完成
• Operator ability to maintain area cleanliness during process operations
操作员能在工艺操作过程中保持作业区的整洁
• Effectiveness of cleaning for the facility and its equipment
清洗整理设施设备的高效性
This monitoring is typically performed in areas and during operations where product is potentially exposed to environmental or operator contamination, however, it is not always included for closed systems since the results may not have a correlation to product impact.
监测通常在某区域,操作过程中产品可能遭受来自环境或人员的污染,但结果与产品并无相互联系,因此并不总是在封闭系统内进行。
Process-related monitoring may include surface and air sites near aseptic connections or product transfer steps. The manufacturing operations monitored may occur in an open room, under laminar flow, or within a "closed" system. Sites should be chosen to demonstrate process integrity in both "open" and "closed" processes. Sample sites and levels also should be chosen to provide meaningful data about a given operation. As an example, nonviable particle counts taken during loading of powdered media into a vessel in a Class 100,000 area may not provide data that is indicative of process quality. Non-viable particle counts taken during aseptic processing operations (excluding powders) in Class 100 areas may provide more valuable information about process control.
工艺相关监测可能包括接近无菌连接或产品转移处的表面和空气位置。生产监测可能发生在层流下的开放空间,或是在一个封闭系统内。位置的选择应能证明“开放”及“封闭”工艺的完整性。采样点和采样水平也应对指定操作能提供有意义的数据。例如,将粉末状培养基装入10万级的容器中进行的非活性例子计数可能无法提供数据来表明工艺质量;但若在100级的无菌工艺中(除粉末外)进行计数,则可能对工艺控制提供更具价值的信息。
The subsequent purification/bioburden reduction steps in a process may also impact the degree to which in-processing testing is warranted. Test frequencies for batch-related, in-process monitoring may differ from those for routine area monitoring. In many cases, environmental monitoring performed in conjunction with batch production activities may fulfill the requirements for routine area monitoring.
工艺中随后的净化/生物负荷削减措施也在一定程度影响过程中测试。与批有关的过程中监测的测试频率不同于那些常规区域监测。在很多情况下,环境监测和批生产活动同时进行可以达到常规区域监测的要求。
Surface and viable air samples that select for the host organism may be appropriate in a fermentation/recovery process area. This data may help to demonstrate process integrity and/or cleaning effectiveness during a product changeover.
这些表面和活性空气样本的宿主生物体也很适合在过程领域中发酵/复原。这些数据有助于说明产品改变过程的完整性和/或清洗效果。
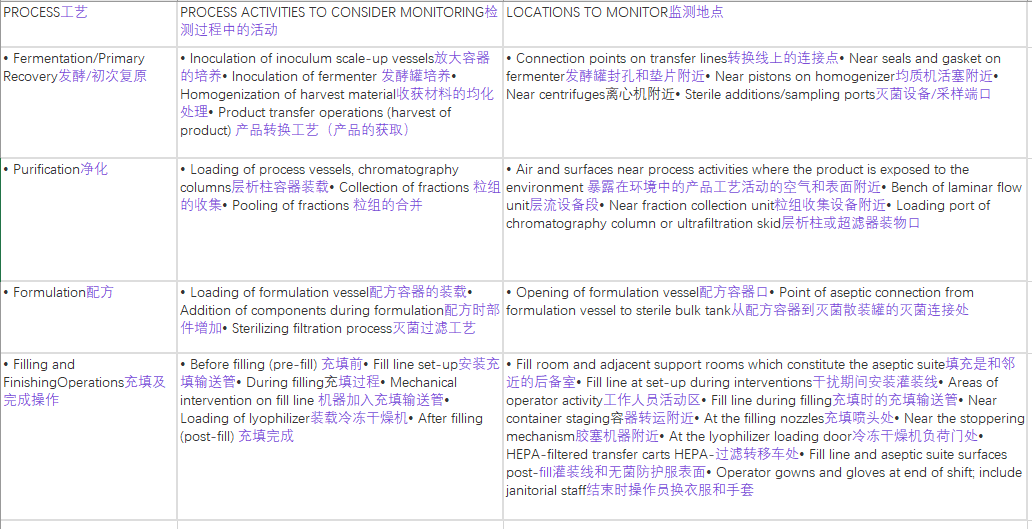
The following table describes examples of different activities and possible sampling locations. The table is not meant to be all inclusive.
下表描述了不同活动及其可能的取样位置(不能涵盖所有)。
Process-related environmental monitoring activities and locations.
工艺相关的环境监测活动和选址
文章来源:药品微生物检测
本网站刊载的所有内容,包括文字、图片、音频、视频、软件等,如非标注为“原创”,则相关版权归原作者所有,如原作者不愿意在本网站刊登相关内容,请及时通知本站,我们将第一时间予以删除。